Enterprise Data Security: How Secure Is Your Company’s Data?
Are you worried about your enterprise data security? Perhaps your company went through a period of immense scaling, and now you are concerned about the security of your enterprise data. Just a single data leak can ruin your company’s reputation.
In this article, we’ll cover the different aspects of enterprise data security and provides you with must-know techniques to protect your data. We’ll also discuss how you can leverage process definition and process automation to improve your data security. Finally, let’s get innovative and look at the potential of blockchain technology to aid enterprise data security.
First, let’s lay the groundwork by discussing the main types of enterprise data security.
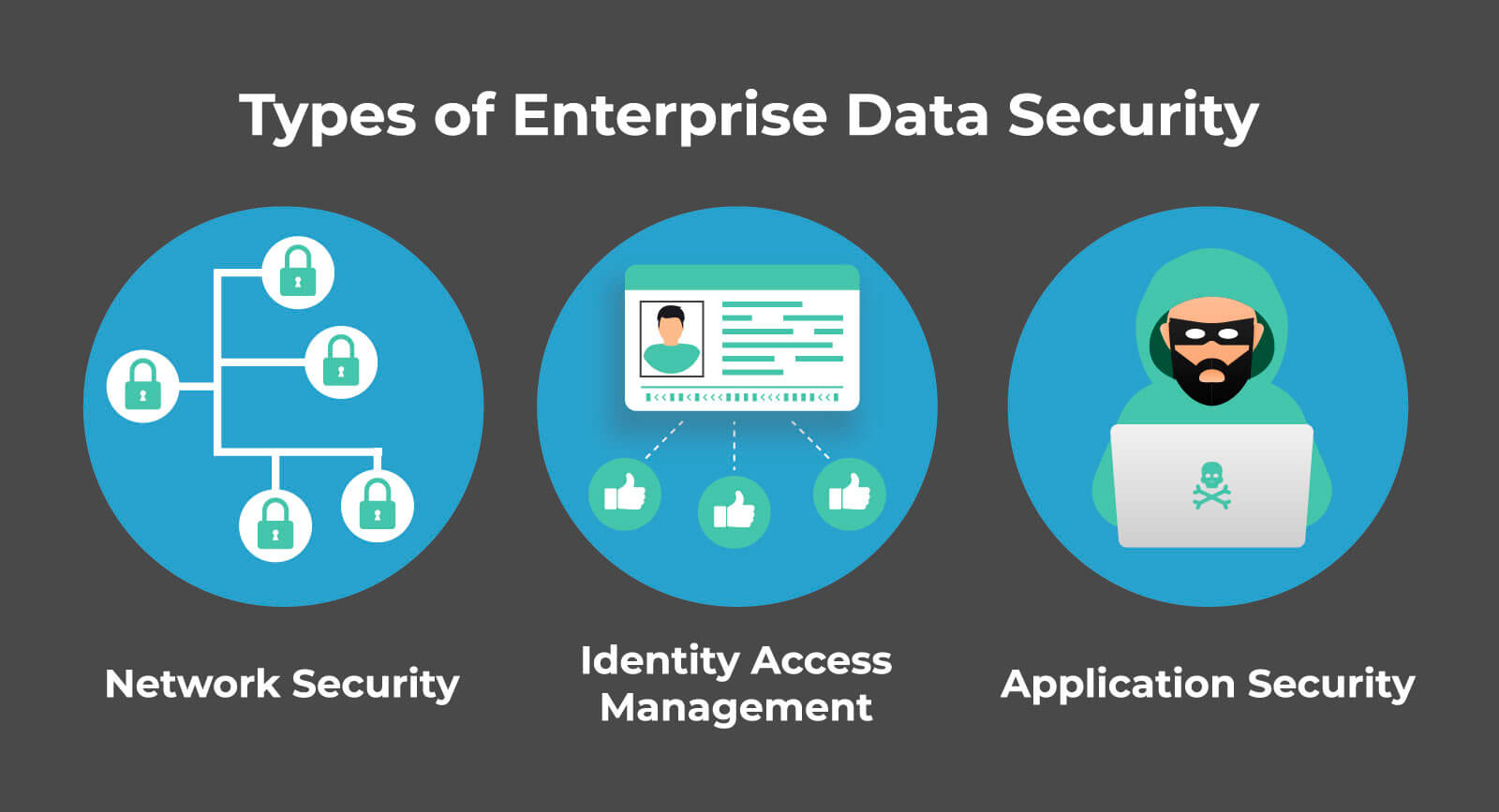
What Are the 3 Main Types of Enterprise Data Security?
Your company data needs to be protected, but do you know where to start? Security is a big field, and it’s easy to get lost. Here are the three main types of enterprise data security you should consider.
1. Network Security
First, let’s get things started by verifying your network security. Network security encompasses many different aspects, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems. In short, network security tries to prevent unauthorized access to your company’s data and includes the security of all data that travels across your network.
Success: Palo Alto Networks exemplifies adequate network security by placing an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) just beyond the firewall to scrutinize incoming data and take necessary automated actions against potential threats. This strategy prevents unauthorized access and minimizes the impact on network performance.
2. Identity & Access Management
Strict control over the users who can access data and resources within your organization is crucial. Unauthorized access leads to data breaches or data theft. As an organization, these data-related security incidents are some of the worst for a company’s reputation.
To dig a bit deeper, most companies use role-based access management (RBAC), which is a solid security pattern for evaluating whether a user should get access to a specific resource. It’s an easy model to implement, and loads of tooling exists that supports it. Besides that, the RBAC pattern fits well with audit and compliance reporting requirements, as you can monitor and track all authorization events.
Failure: The Equifax hack is an example of a failed RBAC implementation. One affected system was an online dispute portal, which allowed attackers to execute system-level commands. Due to an incorrect implementation of RBAC, the online dispute portal had admin rights on dozens of databases. These incorrect access rights allowed the attackers to send 9,000 queries to capture the personal information of roughly 145 million people. To make it clear, Equifax should have implemented proper RBAC for the online dispute tool.
Beyond that, the attackers sending out 9,000 queries to several databases went unnoticed, meaning their intrusion detection and monitoring systems weren’t doing their job — detecting intrusions. In short, while RBAC is a great design pattern for accessing resources, mistakes can still be made when implementing it.
3. Application Security
Application security focuses on preventing software application vulnerabilities as a means to prevent data leaks. Continuous monitoring tools can help you watch for suspicious activities within software applications. For example, these tools can detect unusual access patterns, large outbound data transfers, or signs of tampering.
Success: Snowflake is a great example of a continuous monitoring tool. It showcases the strength of continuous monitoring and threat detection. It captures logs and security data, allowing for advanced threat detection. This enables organizations to continuously monitor their networks, systems, and applications to quickly identify and respond to security threats.
So, what are the best techniques to protect your data?
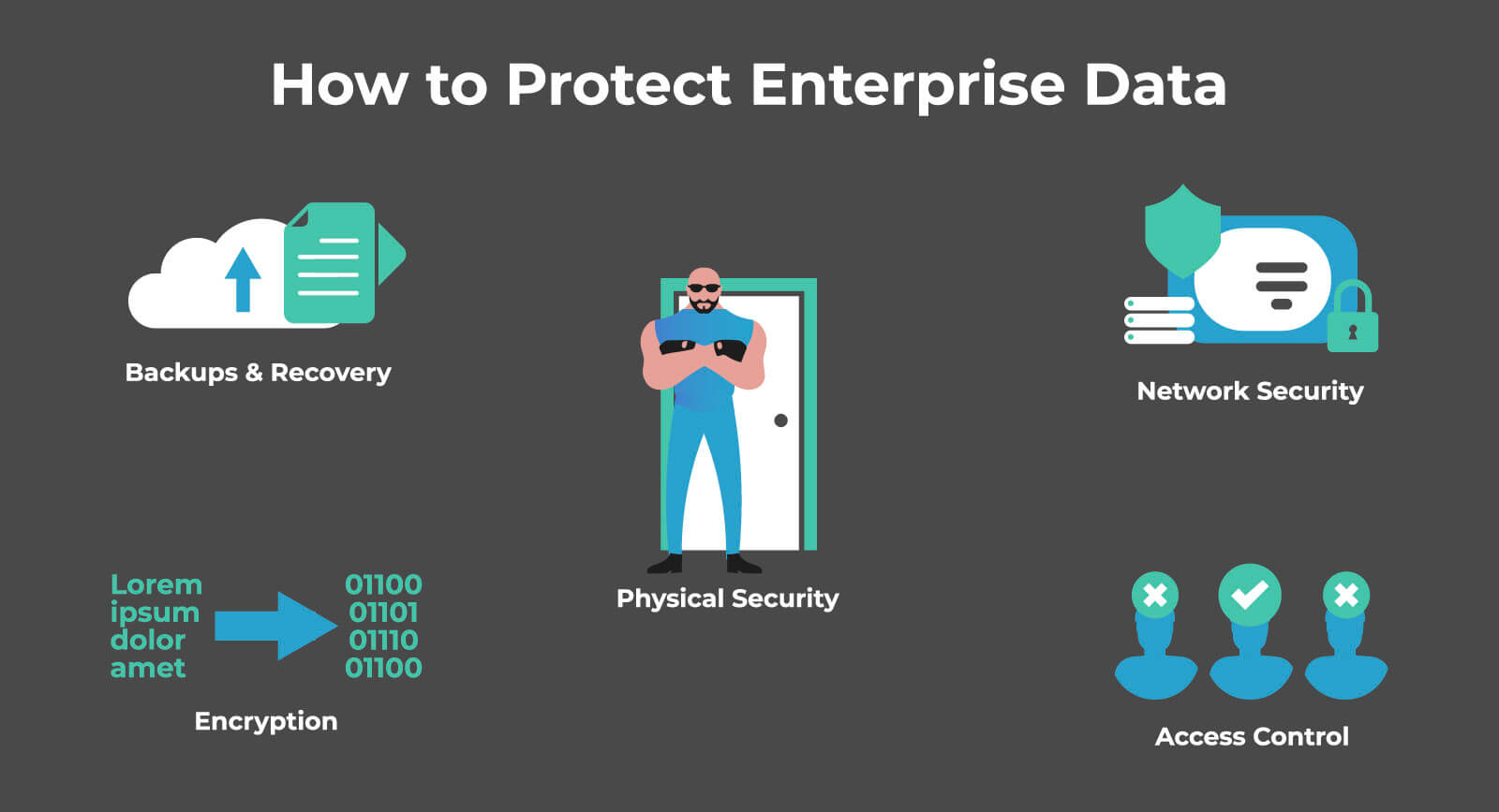
The Best Techniques to Protect Enterprise Data
Encryption
Encryption is the cornerstone of enterprise data security. Whenever you transmit data from one device to another, it’s a best practice to use encryption. Encryption works by converting data into a coded format requiring a decode key. If your data gets intercepted by an unauthorized person, it can’t be read.
However, make sure to use the proper industry-standard encryption mechanisms. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is recommended for all data at rest, and Transport Layer Security (TLS) is recommended for data being transmitted between devices.
Access Control
As previously mentioned, implementing identity and access management (IAM) systems helps you ensure that only authorized parties can access to your data. It allows organizations to control access based on roles to ensure fine-grained data control.
Consider implementing the principle of ‘least privilege,’ where users are given the least amount of access rights necessary to carry out their jobs. Unlike the Equifax breach mentioned earlier, you don’t want to give each person and tool admin rights to all of your critical databases. It’s like opening all your company’s doors and inviting unauthorized people to steal your sensitive data — don’t do that, folks!
Network Security
Network security consists of defending the edges of your network as well as your internal network. A firewall can block unauthorized access to your enterprise data. Internal network security relies heavily on monitoring and anomaly detection.
To tie back to the Equifax hack, it’s unusual when a dispute portal makes thousands of requests to sensitive databases without needing it. Internal network monitoring should detect these anomalies to prevent unwanted data access.
Backups & Recovery
You might be surprised to hear that backups are essential to enterprise data security. However, it would help if you were always prepared for the worst. What do you do when you lose all your data? You’ll be glad to have a few backups to minimize your organization’s data loss. Beyond regularly backing up sensitive data, let’s discuss a disaster recovery plan.
It’s an excellent first step to have data backups. However, we need to discuss what steps to take to get your processes back up and running, restore your data, and find the cause of the data loss or breach. Formulate strategies for dealing with different types of disasters, such as cyber-attacks, natural disasters, or system failures. A well-defined disaster recovery plan will save you a significant amount of time when disaster strikes — literally.
Physical Security
Physical security is often overlooked but equally critical. It includes managing physical access to your buildings, surveillance, and/or installing security personnel. Companies can employ blue teams, which are groups of security experts who try to proactively defend against potential physical or digital attacks. They are a handy resource to adopt a proactive security mindset.
In short, your digital security is only as strong as your physical security. Organizations often overlook this when protecting their enterprise data.
Process Definition in Enhancing Enterprise Data Security
Why? Now, let’s move beyond technical measures to define security processes. You should invest in defining processes to protect enterprise data as an organization. However, it continues further. You need to invest in continuous security education and develop a security-aware culture. When every employee understands how they can safely deal with enterprise data, it significantly reduces risk.
How can you set yourself up for success? A well-defined data security process should define all necessary steps, from data access to data deletion. Each step must be understandable and accessible for employees across different roles to execute.
Security frameworks like ISO 27001 and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) offer systematic approaches to managing sensitive company information.
- ISO 27001 focuses on establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, maintaining, and improving an information security management system (ISMS). It provides a checklist of controls that need to be considered and a risk assessment and mitigation process. In short, it not only focuses on process definition but also on operating and monitoring your processes.
- NIST offers standards and guidelines for managing cybersecurity risks. It focuses on five core components: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. This standard can help you tailor your processes to your organization’s needs.
Pitfalls? Be aware that you can have too many processes, which can lead to frustrations or confusion. Your employees will need help remembering dozens or even hundreds of data-related processes. What do you do when you have so many processes? Well, it might be the right moment to start looking at automating part of your enterprise data security strategy. The following section examines leveraging blockchain technology to automate certain parts of your enterprise data security strategy.
Integration of Technology: The Role of Blockchain
Blockchain technology can automate certain aspects of data security to address the challenge of managing extensive security processes. Data security automation would reduce the burden on employees of learning and executing many data-related processes.
Automation & Security: First, blockchain technology can automate the enforcement of data security policies by embedding rules into smart contracts. For instance, it can automatically enforce data access or data compliance and log data access requests on the ledger. Another example is embedding data privacy regulations into smart contracts to adhere to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Further, the immutable ledger lends itself well to creating audit reports on data access. This eliminates the need for human intervention and minimizes the risk of human error.
Decentralized & Immutable: Blockchain’s decentralized nature removes the single point of failure, which enhances data security. Every data record stored on the blockchain is immutable. In a disaster, recovering your company’s data from the blockchain would be relatively straightforward.
Imagine a scenario where your company suffered from a cyberattack or natural disaster. Traditional systems often store data in a single physical location, making them a single failure point. When your company’s data is stored on the blockchain, each node in the network contains a copy of your data. Therefore, blockchain technology simplifies the process of disaster recovery as you can quickly access your data and instantiate your systems.
Concluding Enterprise Data Security
Organizations should clearly define data processes. However, it’s crucial to avoid overwhelming users with processes. It’s best to look at data security automation tooling or tools that leverage blockchain technology. These can reduce the burden on your employees so they can continue focusing on their jobs.
Beyond processes, education plays a vital role in your enterprise data security. Continually educate your employees on the latest data security risks so they know the DOs and DON’Ts of enterprise data.
As organizations grow, so do their enterprise data security needs.
